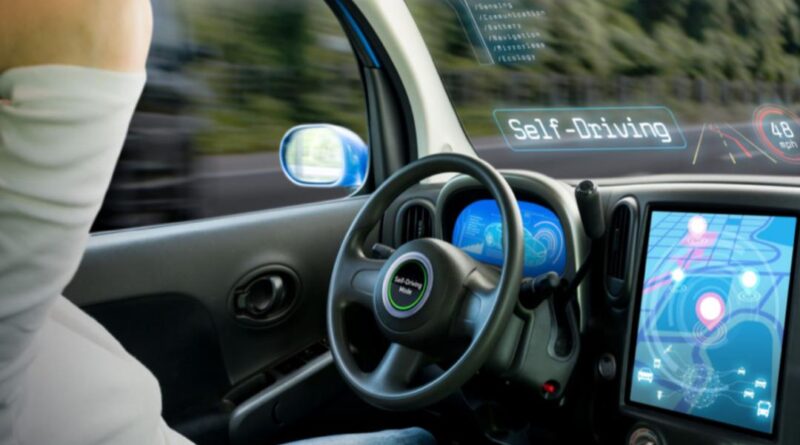
What You Should Know About AI-Powered, Eco-Friendly Self-Driving Cars
Self-driving cars, also known as autonomous vehicles, are among the most transformative innovations in today’s tech-driven world. These vehicles, which operate without a human driver by using Artificial Intelligence (AI), are designed to reduce traffic accidents, streamline travel, and improve the overall quality of life. Despite their potential, however, they also raise concerns regarding safety, regulation, and public acceptance.
AI-powered vehicles are equipped with advanced systems that enable them to detect their surroundings, determine routes, and make real-time decisions — all without human intervention. They rely on a combination of sensors, cameras, GPS, radar, and machine learning algorithms to navigate safely and avoid obstacles, including other vehicles, pedestrians, and road barriers.
The core of these vehicles is Artificial Intelligence (AI), which mimics human decision-making. By continuously collecting and analyzing data, these cars learn and adapt to various road conditions, ensuring both safety and efficiency in transportation.
The concept of autonomous driving isn’t entirely new. The first experiments with self-driving technology date back to the 1980s, with early prototypes tested in controlled environments. However, significant progress began in 2009 when Google launched its Waymo project. This initiative marked the first major step toward creating commercially viable autonomous vehicles powered by artificial intelligence.
Since then, companies like Tesla, Uber, Apple, and other tech giants have invested heavily in developing self-driving technologies. Today, such cars are being tested and used in cities across the United States, parts of Europe, and Asia, as governments slowly adjust their transportation laws to accommodate this technological leap.
One of the major advantages of self-driving cars is their potential to protect the environment. Many of these vehicles are fully electric, which means they produce zero carbon emissions. This makes them a key solution in the global effort to combat climate change and reduce air pollution in urban areas.
Furthermore, AI systems can optimize driving patterns—reducing unnecessary braking, idling, or fuel consumption—which leads to more energy-efficient transportation overall. When combined with smart traffic systems, these vehicles can significantly ease congestion and limit environmental degradation caused by traditional fuel-powered cars.
Despite the benefits, self-driving cars also face significant challenges. Safety remains a top concern, especially in unpredictable traffic situations or poor weather conditions. There have been reported accidents involving autonomous vehicles, leading to public skepticism and legal scrutiny.
Another concern is the legal framework surrounding these vehicles. Since traffic laws vary from country to country and even state to state, regulating autonomous vehicles is complex. Questions around liability in the event of an accident—whether it’s the fault of the car manufacturer, the AI system, or the user—remain unresolved in many regions.
Additionally, widespread adoption may impact jobs, particularly for professional drivers. Governments and industries will need to find ways to manage this shift in employment.
AI-powered self-driving cars represent the future of mobility. As technology evolves, these vehicles are expected to become more accessible, safer, and more

By:Florence Uwamaliya
![]()




